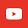
Path to globalisation for Chinese companies
Chinese companies develop their overseas businesses mainly through cross-border M&A and greenfield investment. There are typically four stages of development, and companies should adopt different human capital management approaches according to the development characteristics at different stages:
- Initial stage - preliminary internationalisation: Centralised control from the head office, with expatriate staff sent overseas to support the rapid expansion of local business and to achieve efficient control from the head office.
- Expansion stage - international companies: Establish overseas management companies or departments to specialise in the management of overseas subsidiaries and meet the growing demand for international talent through the transfer of knowledge and experience and cross-regional talent flow.
- Deepening stage - multinational companies: With the gradual localisation of R&D and production lines, the head office differentiates the management of overseas companies at different stages of development and in different regions, and expands local teams to replace large-scale staff expatriation.
- Leading stage - global companies: The head office is gradually streamlined and transformed to assume the overall control and coordination of overseas regions and companies, and to unify the deployment of talent across regions by building a global talent management system.
Human capital challenges in the globalisation process of Chinese companies
Challenge 1: Comprehensive identification of the target company’s HR issues in an M&A transaction
When conducting overseas mergers and acquisitions transactions, enterprises often face various challenges in human capital management due to differences in cultures, regulatory environments, and labour requirements in different regions and countries. For example, organisational set-up and control methods may not be suitable to support the rapid development of overseas business; loss of core talent due to insufficient communication or cultural differences; imposing the company’s own culture on the acquired enterprise may lead to cultural conflicts and hinder the business synergy and integration between the two parties; unfamiliarity with local labour laws may lead to employment compliance risks. These issues may lead to the failure to realise the value of the deal or even deal failure.
Challenge 2: Establishing a global HR system and professionalising HR management
At the level of HR operations, companies fail to develop a HR management model that is suitable for local development or lack a global HR control and operating system, which makes it difficult to align their overseas HR operations such as recruitment, training, performance assessment, compensation and benefits, and union negotiation, with international standards. The lack of differentiated management, control systems and employment strategies, has prevented human capital management from becoming professional and global.
Challenge 3: Building a HR system to establish effective overseas management
Due to geographical limitations, it is often difficult for head office to manage overseas subsidiaries. The globalisation and digitisation of information is crucial for overseas companies to coordinate and efficiently manage their human capital. How to build a global and digital HR system that is compliant, accurate, visible, and real-time, so that the head office can have a grip on human capital management of overseas subsidiaries is an urgent issue for most overseas companies.
Challenge 4: Forming a differentiated control system and develop global talent and helping to manage human capital overseas
Overseas businesses are laid out in different regions and are varied in scales and maturity. Adopting a ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach to management may affect overseas efficiency. From the perspective of the head office, it is important to balance the consistency and differences in the control of different overseas businesses and the challenges of ‘what to control’, ‘how deep to control’ and ‘how to control’ are the challenges of differentiated management of overseas businesses.
At the same time, in the process of going overseas, companies often lack the identification, cultivation, and retention of global talent. However, as the overseas business has grown to a certain scale, the shortage of global talent is often a significant factor limiting the global expansion of companies.
Companies need to establish a global talent management system to systematically manages all aspects of talent profiling, selection, recruitment, training, incentives, expatriation and repatriation to form a global talent pool that can efficiently support cross-regional talent allocation and enable rapid overseas business development.
Our services
To address these challenges, we focus on three key scenarios and form four main categories of products and services, aiming to provide end-to-end solutions for companies to build their global human capital management capabilities and to ensure a smooth transition when ‘going overseas’.
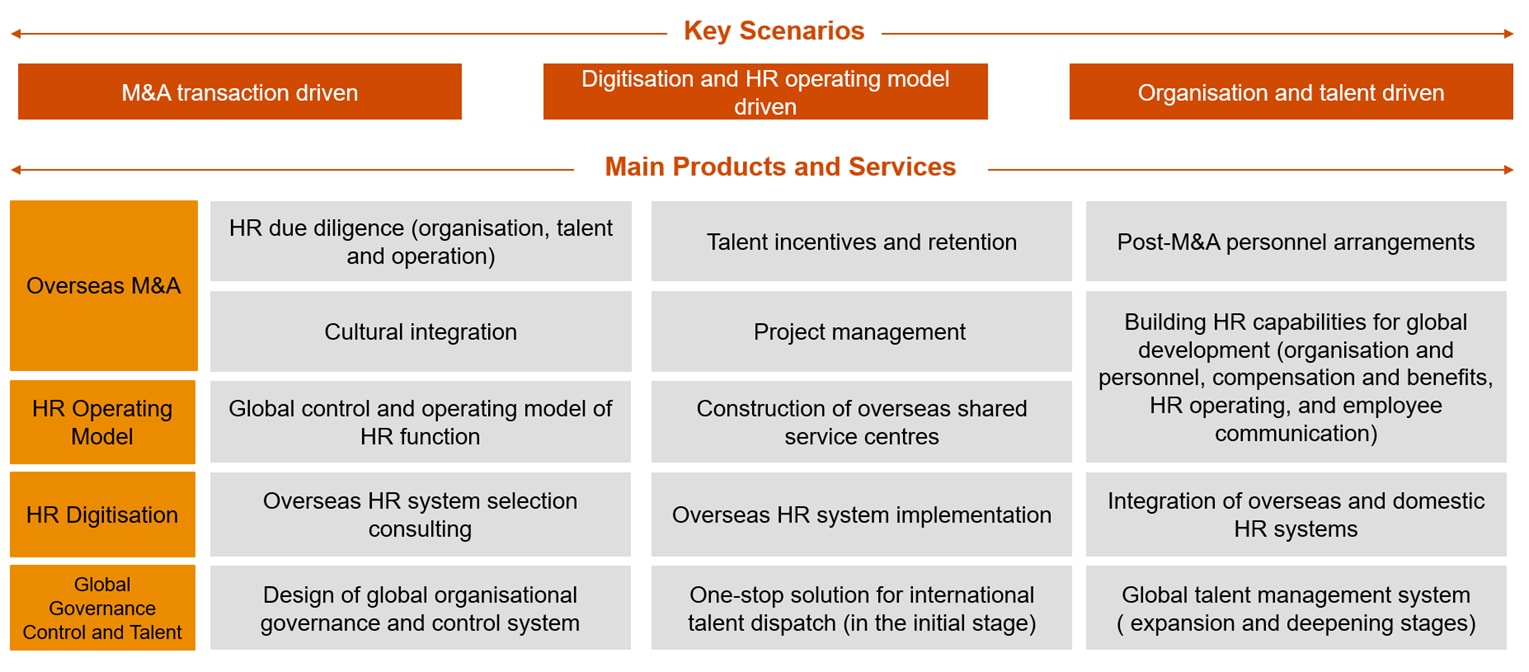
HR due diligence (organisation, talent and operation): Assist companies in conducting due diligence on the target company's organisation, talent, compensation and benefits, employment compliance, HR capabilities, etc. to fully identify HR-related risks, providing key information input for investment and M&A decisions, transaction agreement signing, delivery preparation, and post-M&A integration.
Talent incentives and retention: Assist companies to identify key talent in target company through various dimensions (e.g. importance of deal success and importance of strategic development, etc.) design targeted retention and communication plans to retain core talent and ensure personnel stability of the target company.
Post-M&A personnel arrangements: Assist in designing and implementing personnel transfer or termination plans. Help companies to effectively avoid compliance and public opinion risks during the process and reduce the impact of personnel transfer or termination on the stability and continuity of the target company.
Cultural integration: Using PwC's organisational DNA model to design a cultural survey questionnaire for the company and analyse the similarities and differences between the cultures of both parties through culture research. Combining the integration objectives of the company, the strategic development requirements for the target company, the local cultural background, and the results of the cultural research to determine suitable cultural integration model and measures, and assist in the implementation.
Project management: As the Project Management Office (PMO) during the M&A process, identify the main work streams, lead the development of the integration plan, and create the project blueprint; coordinate the working groups, manage the project progress, resources and risks, and ensure delivery. Manage the mindset and expectations of various stakeholders throughout the project advancement process and promote a clear understanding and willingness of all parties on integration and synergy and reach consensus on work direction.
Global control and operation model of HR function: Assist companies to design the global management plan and operation model for HR functions based on the depth of control and management requirements of the head office on various overseas subsidiaries. Plan the scope of control and content of the head office around the ‘selection, implementation, cultivation and retention’ of human resources, clarify which aspects require standardised management, and which aspects allow for differentiation, in order to establish a HR functions management model that aligns with local conditions.
Construction of overseas shared service centres: Guided by the company's globalisation strategy, assist the company to build overseas shared service centres through global HR service planning, control design of sharing model, organisational design, process design and system implementation, to strengthen the standardisation and professionalisation of global HR services, and improve management efficiency of global HR.
Building HR capabilities for global development: Assist companies to build a full set of solutions for HR in global development scenarios in terms of organisation and people, compensation and benefits, HR operations, employee communication, etc., precipitating key competencies, and providing support for companies to cultivate relevant talents.
Overseas HR system selection consulting: Analyse the HR system selection requirements and objectives in six dimensions: business development stage, key business support, existing pain points, high frequency business occurrence points, key user concerns, and overseas HR operational characteristics. Using PwC’s system selection tools to evaluate the functionality, structure, technical performance and user experience, to assist companies in selecting the suitable HR system.
Overseas HR system implementation: Assist companies to sort out system structure principles and formulating system building plans. Based on local management and data compliance requirements, business priorities, implementation urgency and maturity and task dependencies, plan the system implementation path and schedule, and ensure the system launch is executed as planned.
Integration of overseas and domestic HR systems: Assist companies to achieve global system integration to meet compliance, security, reliability, real-time, versatility, and stability requirements, enabling them to access overseas HR data in a timely manner and form substantive control over overseas human capital.
Design of global organisational governance and control system: Assist companies in determining the control model to be adopted for different stages of development and business characteristics of overseas businesses, based on the six dimensions –strategic positioning, implementation path, business maturity, business relevance, business expertise, and business risks to achieve differentiated control of different stages and businesses. Assist companies to understand local corporate governance requirements, adopt a market-oriented governance model, and implementing control over overseas subsidiaries through the board of directors.
One-stop solution for international talent dispatch: Assist companies in developing a global talent demand profile, talent selection mechanism and talent dispatch mechanism, forming a systematic talent dispatch solution in the initial stage of enterprise internationalisation.
Global talent management system: In the stages of international expansion and deepening, the demand for global talent is rising rapidly. We assist companies to establish systematic talent selection standard, designing effective assessment and incentive mechanisms for dispatched talent, formulate clear global talent development paths and retain returning talent upon expiry of their overseas assignment, in order to comprehensively address global talent development problems from the perspective of talent selection, implementation, cultivation and retention.
Our past experiences
PwC has been at the forefront of providing global human capital management services to a number of companies:
Assisted a major domestic home appliance group to acquire the white goods business of an electrical group.
- Due diligence: Provided HR due diligence services, focussing on the impact of manpower costs or liabilities on the transaction consideration, transfer of benefit plans, core talent retention and incentive, cultural differences, corporate governance and control, etc., to identify transaction risks and provide input for agreement negotiations and post-delivery integration.
- Governance and control: Assisted the client in defining the principles and objectives of governance and control design for the target company, building a governance structure, designing a synergy-oriented strategic control model, refining the division of authority and responsibility for each function under the control model and forming a comprehensive control list.
- Cultural integration: Assisted the client in conducting cultural research to gain a deep understanding of the current cultural situation, differences and future expectations of the target company; developed a cultural integration model, clarified objectives and principles, and developed integration measures to address key cultural differences for better implementation.
- Organisational support mechanism for business synergy: Established a business synergy project management office with clarified project operating mechanisms. Assisted both parties in identifying synergy opportunities, quantification of synergy values, and tracking and managing of synergy benefits.
- Project management: Established a project management office to oversee the entire transaction and assisted the client in coordinating the work of the seven consulting firms and monitored the progress of the project. Assisted the client with their integration plan and a 100-day plan to help realise the transaction value.
Established a modern overseas assets governance and control system for a state-owned enterprise with global operations.
- Top-level design of the institutional system: Assisted client in improving the top-level design of their global institutional system, incorporating the Party's overall leadership into corporate governance, undertook the management will and control requirements of higher-level units, analysed the management positioning and control mode of companies in different regions, and clarified the path and blueprint for improving the institutional system.
- Management boundaries and authorisation: Based on the client's own management mode positioning, reviewed the current management authorisation system, analysed differentiated control requirements, and summarised the head office’s management boundaries and authorisation system.
- Global process reshaping and institutional optimisation: Benchmarked international first-class companies in terms of governance model, management authorisation, growth path, institutional system, support and protection. Reshaped global governance and control processes, consolidated and formed a hierarchical and complete process structure and optimised the existing 27 global management systems for the client.
- Planning of institutional management information technology: Created a one-stop global institutional management information system to meet the client’s digital transformation needs.